Datasets Overview
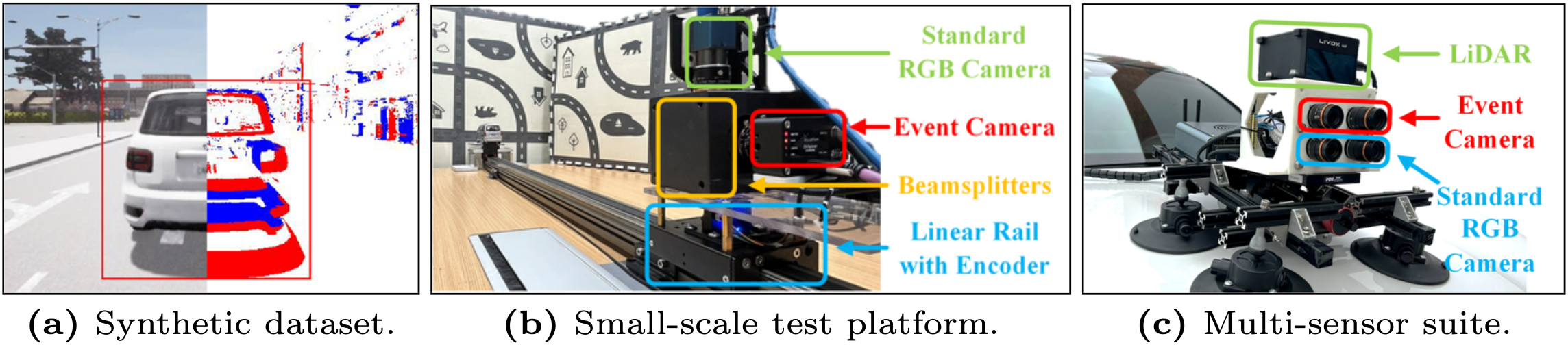
Predicting a potential collision with leading vehicles is an essential functionality of any autonomous/assisted driving system. One bottleneck of existing vision-based solutions is that their updating rate is limited to the frame rate of standard cameras used. In this paper, we present a novel method that estimates the time to collision using a neuromorphic event-based camera, a biologically inspired visual sensor that can sense at exactly the same rate as scene dynamics. The core of the proposed algorithm consists of a two-step approach for efficient and accurate geometric model fitting on event data in a coarse-to-fine manner. The first step is a robust linear solver based on a novel geometric measurement that overcomes the partial observability of event-based normal flow. The second step further refines the resulting model via a spatio-temporal registration process formulated as a nonlinear optimization problem. Experiments on both synthetic and real data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, outperforming other alternative methods in terms of efficiency and accuracy.



@misc{li2024eventaidedtimetocollisionestimationautonomous,
title = {Event-Aided Time-to-Collision Estimation for Autonomous Driving},
author = {Jinghang Li and Bangyan Liao and Xiuyuan LU and Peidong Liu and Shaojie Shen and Yi Zhou},
year = 2024,
eprint = {2407.07324},
archiveprefix = {arXiv},
primaryclass = {cs.CV}
}