Synchronization
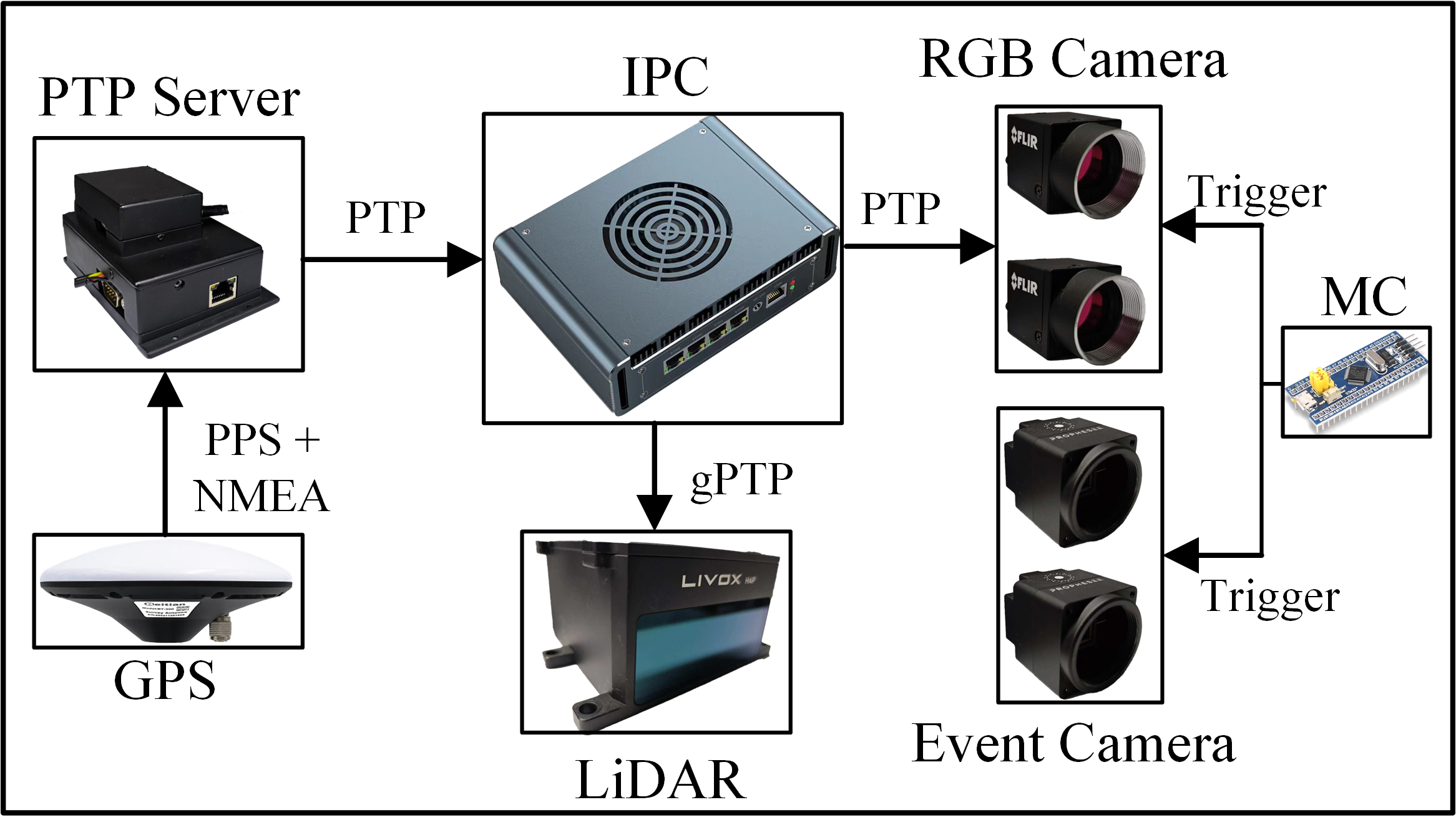
We synchronize all sensors in the sensor suite at the
hardware level. To this end, we utilize Precision Timing
Protocol (PTP) and the generalized Precision Time
Protocol (gPTP), which can provide sub-microsecond
synchronization accuracy in the Ethernet.
The time synchronization among all the devices is illustrated in Fig. 1. First, we use a PTP server to synchronize
GNSS’s clock with the system clock of the industrial personal computer (IPC). The IPC is then designated as the
master clock, using the PTP protocol to synchronize with
the RGB cameras. Since the Livox HAP only supports the
gPTP protocol, we use gPTP to synchronize between the IPC
and the LiDAR. To synchronize the event cameras with the
system time, we utilize a micro-controller to generate four
synchronization pulses at 20 Hz. These pulses are used to
simultaneously trigger the two RGB cameras and the two event cameras. The RGB and event cameras are configured
in external trigger mode. When the RGB camera receives
a synchronization pulse, it begins to capture an image and
record its timestamp. Meanwhile, the event camera would
also be triggered by the synchronization pulse, immediately
generating a signal with a timestamp. The temporal offset
between the RGB camera and the event camera can be easily
calculated as the difference between the two timestamps. In
addition, the integrated navigation systems UG005 X1 and
CGI-610 are synchronized via their built-in GNSS clocks.